Harnessing Solar Energy for Sustainable Power Generation: A Comprehensive Solar Case Study
A Comprehensive Solar Case Study
1. Introduction:The depletion of conventional fossil fuels and the associated environmental concerns have propelled the world towards the exploration of cleaner and more sustainable energy alternatives. Among these alternatives, solar energy stands out due to its abundant availability and minimal environmental impact. This case study delves into the multidimensional aspects of solar energy, ranging from technological advancements to economic viability and environmental considerations.

2. Solar Technologies:Solar energy can be harnessed through various technologies, including photovoltaic (PV) cells and solar thermal systems. Photovoltaic cells directly convert sunlight into electricity, while solar thermal systems use sunlight to generate heat, which can be subsequently converted into electricity.

2.1 Photovoltaic Cells:Photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar panels, consist of semiconductor materials that release electrons when exposed to sunlight, creating an electric current. Different generations of PV cells, from traditional crystalline silicon to emerging thin-film and organic options, offer varying levels of efficiency, cost, and applicability.
2.2 Solar Thermal Systems:Solar thermal systems encompass a range of technologies, such as parabolic troughs, solar towers, and dish systems. These systems concentrate sunlight onto a central receiver to generate heat, which can be utilized to produce steam and drive turbines for electricity generation.
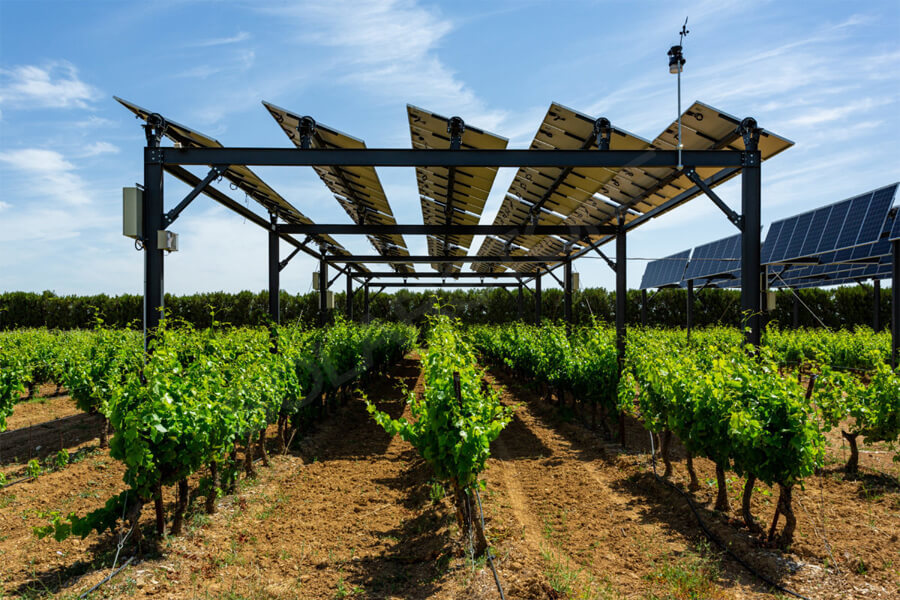

3. Economic Viability:One critical factor in the widespread adoption of solar energy is its economic viability. Over the past decade, the cost of solar technologies has plummeted due to advancements in manufacturing processes and economies of scale.

3.1 Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE):The LCOE of solar energy has reached parity with or even fallen below that of conventional energy sources in many regions. This is particularly evident in regions with high solar insolation and supportive government policies. The decreasing LCOE of solar energy makes it an attractive option for utility-scale and distributed power generation.

3.2 Return on Investment (ROI):Both residential and commercial users are considering solar energy as a means to generate electricity and reduce energy bills. The ROI of solar panels depends on factors such as system cost, electricity rates, available incentives, and the system's efficiency. In many cases, residential solar installations achieve a positive ROI within a relatively short period.

4. Environmental Impact:Solar energy's environmental benefits are a key driver behind its growing popularity. Solar power generation is clean, producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to reduced air pollution and water consumption compared to fossil fuel-based energy sources.

4.1 Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Solar energy systems have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to conventional fossil fuel-based power plants. The emissions associated with manufacturing, transportation, installation, and maintenance are typically offset by the emissions avoided during the operational phase.

4.2 Land Use and Biodiversity:Large-scale solar installations require land for the placement of solar panels or mirrors. While these installations can impact local ecosystems and biodiversity, proper site selection, design, and management can mitigate these concerns. Additionally, the use of floating solar arrays on bodies of water minimizes land use conflicts.

5. Implementation Challenges:Despite the promising potential of solar energy, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption.

5.1 Intermittency and Energy Storage:Solar energy production is intermittent due to variations in sunlight availability. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, are essential to store excess energy during sunny periods for use during cloudy days or nighttime.

5.2 Grid Integration:Integrating solar energy into existing grids poses technical challenges, including voltage stability, frequency control, and grid management. Advanced grid technologies and smart inverters are being developed to address these challenges and ensure seamless integration.
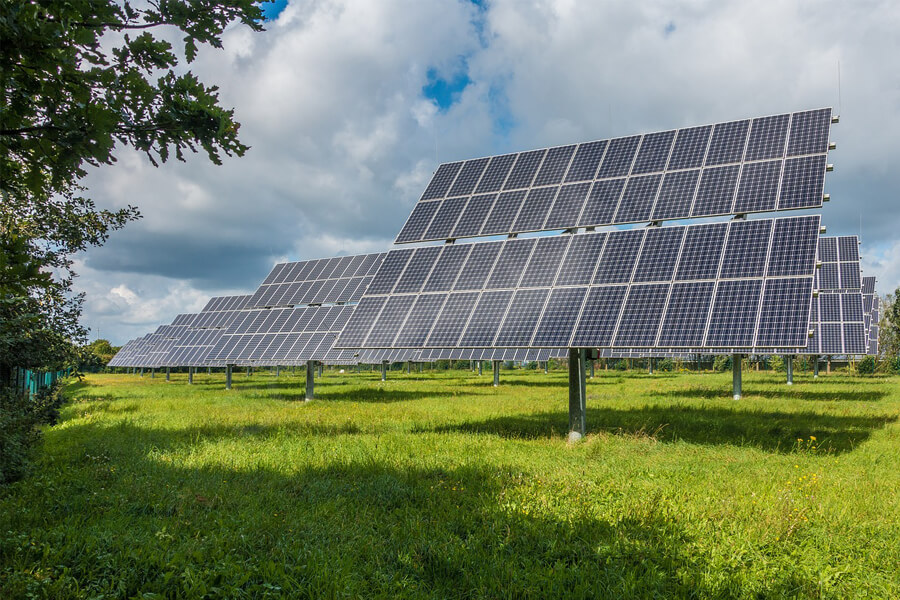

5.3 Material Availability and Recycling:The production of solar panels relies on rare materials such as indium, tellurium, and certain metals. Ensuring a sustainable supply chain and developing efficient recycling processes are crucial to prevent resource depletion and minimize environmental impacts.
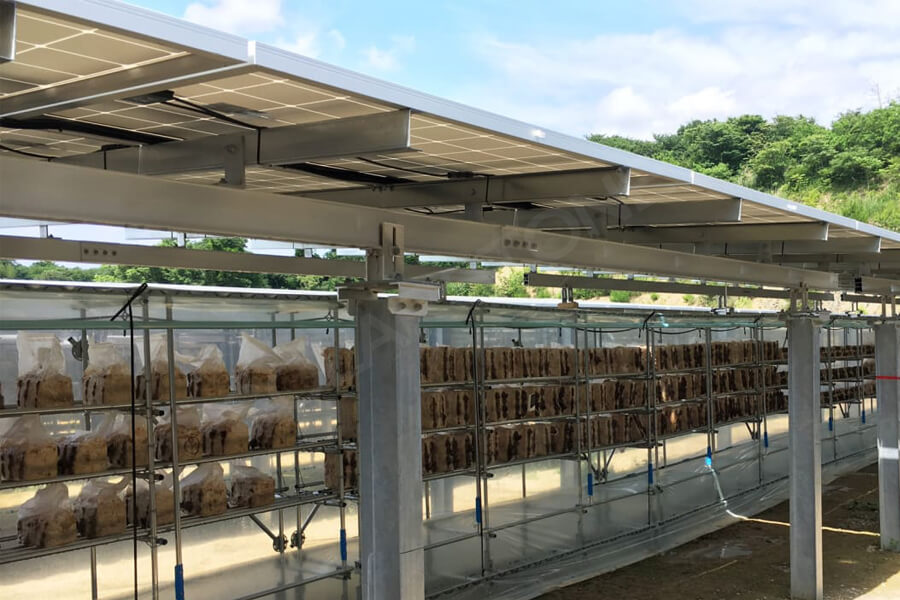

6. Case Study: Solar Energy in Region X:To illustrate the application of solar energy in a real-world context, this case study explores its potential in Region X. The region boasts high solar insolation and a commitment to renewable energy adoption.
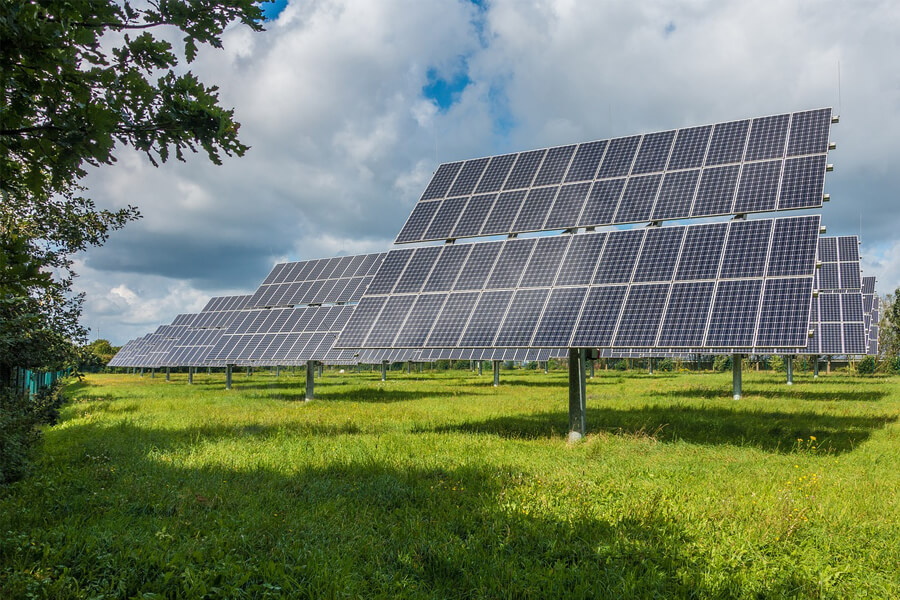

6.1 Solar Resource Assessment:Detailed solar resource assessment is conducted to determine the region's solar potential. Satellite data and ground measurements are used to estimate the solar irradiance, which is a critical factor in assessing the viability of solar projects.
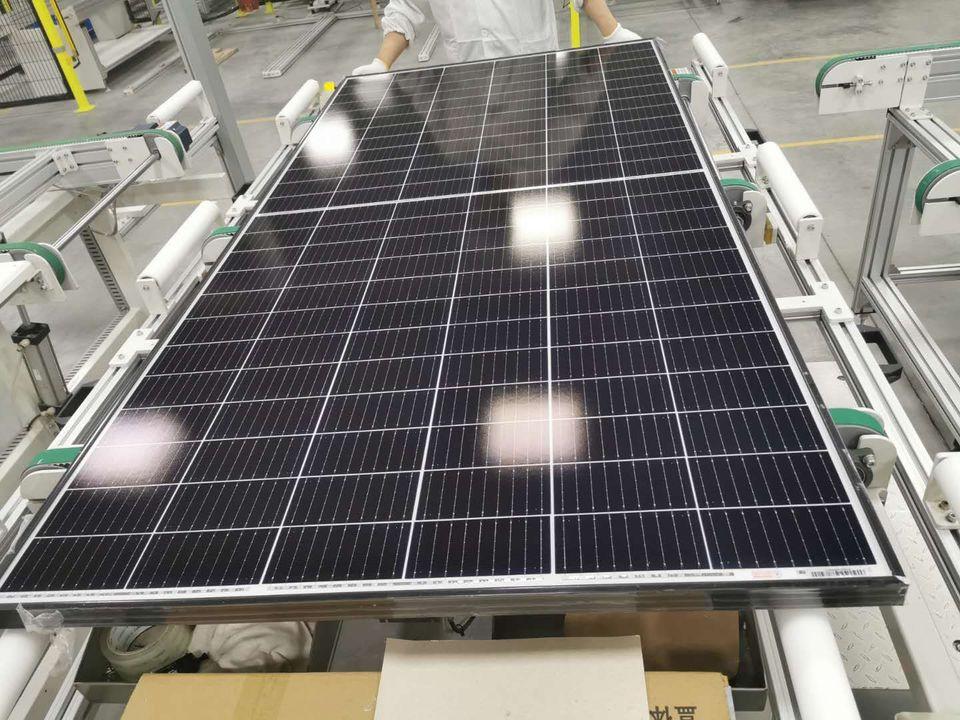

6.2 Policy and Regulatory Landscape:The case study examines the existing policies and regulations that support solar energy adoption in Region X. These policies include feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and net metering programs that encourage investment in solar installations.
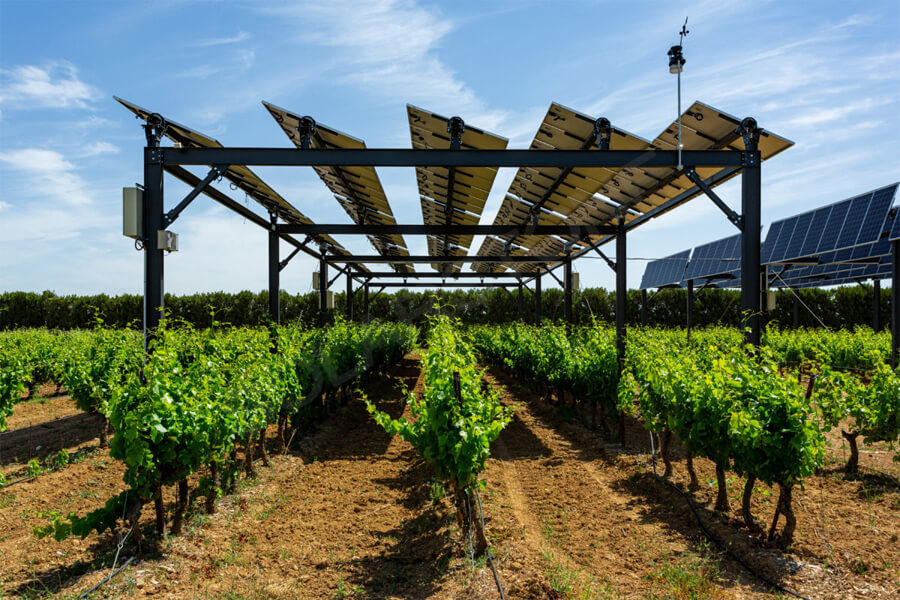

6.3 Community Engagement:Engaging local communities and stakeholders is crucial for the successful implementation of solar projects. Public awareness campaigns, town hall meetings, and collaborative decision-making processes are used to ensure community support.

7. Future Outlook:The future of solar energy holds immense promise. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and overcoming challenges related to energy storage and grid integration.

7.1 Technological Advancements:Emerging technologies, such as perovskite solar cells and tandem solar modules, have the potential to significantly improve efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs. These innovations could drive the next phase of solar energy growth.
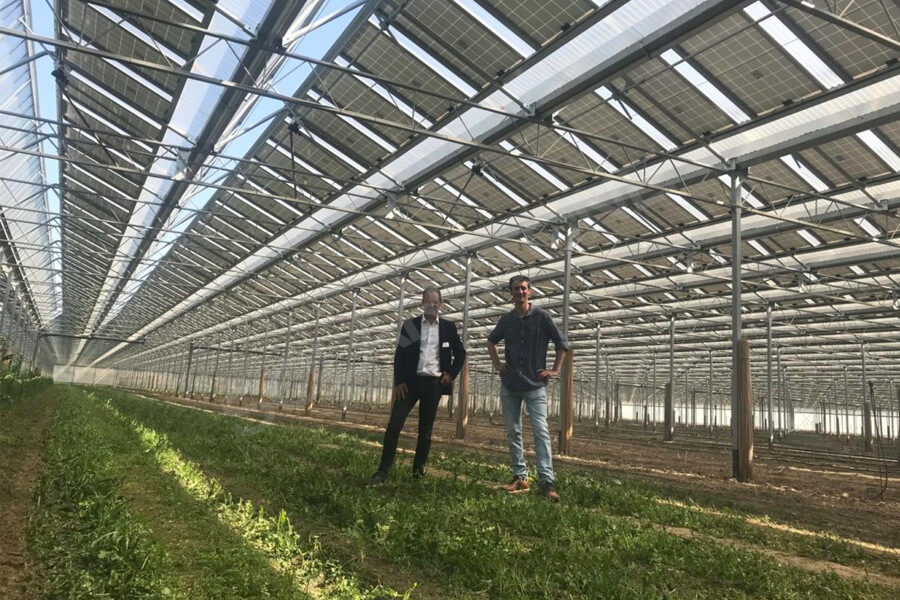

7.2 Energy Storage Breakthroughs:Advancements in energy storage technologies, including next-generation batteries and advanced thermal storage systems, are poised to address the intermittency issue and enable reliable power supply.
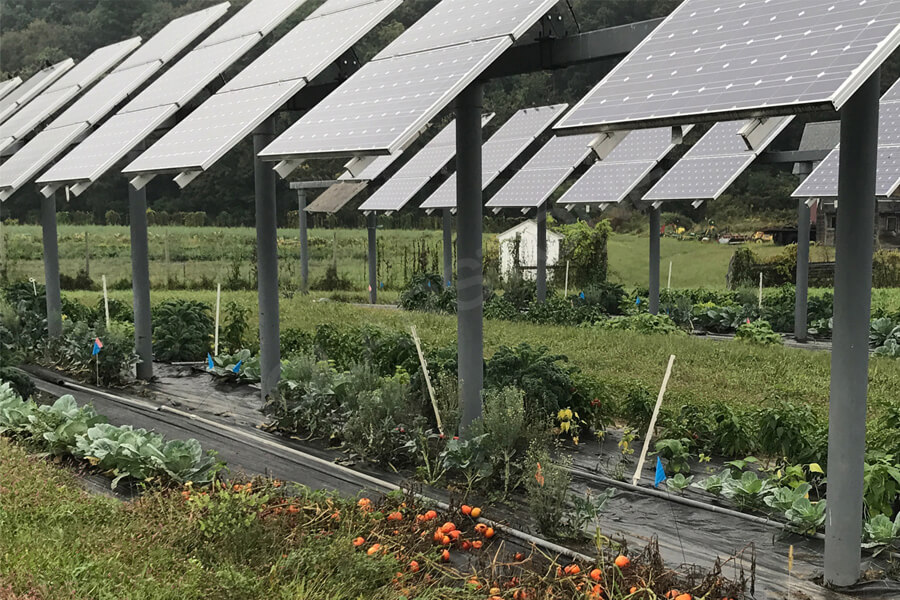

8. Conclusion:Solar energy is a critical component of the transition to a sustainable and low-carbon energy future. Through technological advancements, economic viability, and environmental benefits, solar power has the potential to reshape the global energy landscape. However, overcoming implementation challenges and fostering supportive policies remain essential to unlocking solar energy's full potential. As regions worldwide continue to invest in solar projects, a cleaner and more resilient energy future becomes increasingly attainable.
Follow Us ! TEEJOIN SOLAR Power









