Popular Science: The Basics of Solar Radiation
Solar radiation, often referred to as solar energy resources or simply sunlight, is a generic term for the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. A variety of technologies can be used to capture solar radiation and convert it into useful forms of energy, such as heat and electricity.
However, the technical feasibility and economic operation of these technologies in a given location depends on the available solar resource.

Basic principles
Every place on Earth receives sunlight for at least part of the year. The amount of solar radiation reaching any point on the Earth's surface varies depending on the following factors:
-geographic location
-Time of day
-Season
-Local landscape
-Local weather

Because the Earth is round, the Sun illuminates the Earth's surface at different angles, ranging from 0° (just above the horizon) to 90° (directly overhead).
When the sun's rays are vertical, the Earth's surface receives all the energy possible.The more tilted the sun's rays are, the longer they take to travel through the atmosphere, becoming more scattered and diffuse. Because the Earth is round, cold polar regions never experience high insolation, and because of the tilted axis of rotation, these regions don't see sunlight at all for part of the year.

The Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit and is closer to the Sun during parts of the year. As the Sun gets closer to the Earth, the more solar energy the Earth's surface receives.The Earth is closest to the Sun during the summer in the Southern Hemisphere and during the winter in the Northern Hemisphere.However, because of this difference, the presence of vast oceans moderates the hotter summers and colder winters one would expect to see in the Southern Hemisphere.

The 23.5° tilt of the Earth's rotational axis is a more important factor in determining the amount of sunlight hitting the Earth at a given location. The tilt results in longer days in the Northern Hemisphere from the vernal to the autumnal equinox and longer days in the Southern Hemisphere during the other six months. Around March 23 and September 22 of each year, the day and night at the diurnal equinoxes are both exactly 12 hours long.

Countries at mid-latitudes, such as the United States, get more solar energy in the summer, not only because the days are longer, but also because the sun is almost overhead. During the shorter days of winter, the sun's rays are more inclined.

Cities such as Denver, Colorado (at latitudes near 40°) receive almost three times as much solar energy in June as they do in December.
The Earth's rotation also contributes to the hourly variation in sunlight. In the early morning and late afternoon, the sun hangs low in the sky. When the sun is at its highest point, its rays travel farther through the atmosphere than at noon. On clear days, the greatest amount of solar energy reaches solar collectors around solar noon.
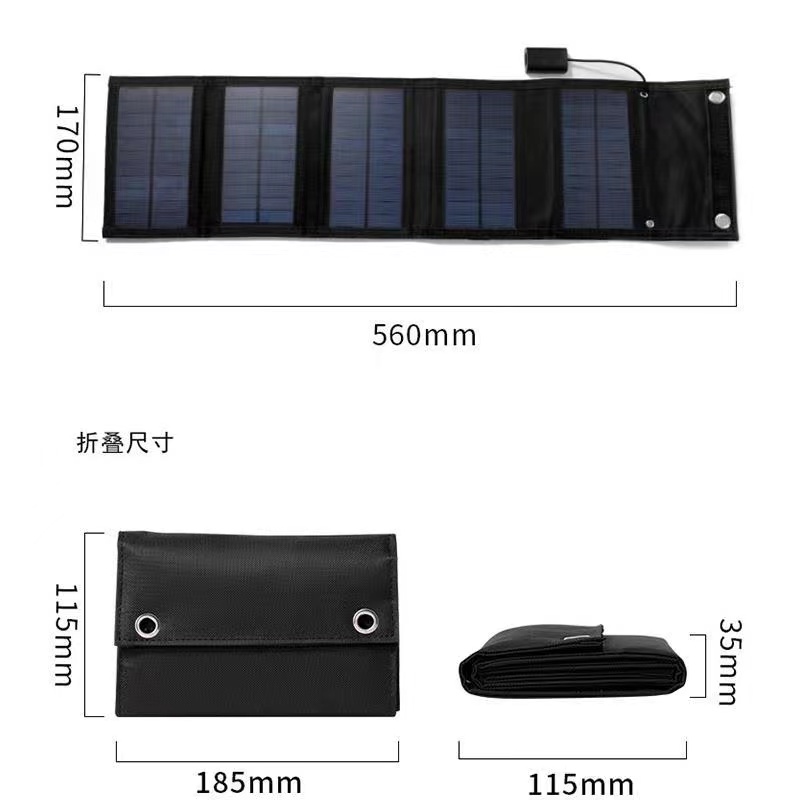

Diffuse and direct solar radiation
As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, some of it is absorbed, scattered and reflected:
-Air molecules
-Water vapor
-Clouds
-Dust
-Pollutants
-Forest fires
-Volcanoes.

This is called diffuse solar radiation. Solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface without diffusion is called direct beam solar radiation. The sum of diffuse and direct solar radiation is called global solar radiation. Atmospheric conditions can reduce direct beam radiation by 10 per cent on clear, dry days and 100 per cent on dense, cloudy days.

MeasurementScientists measure the amount of sunlight that falls on specific locations at different times of the year. They then estimate the amount of sunlight falling on areas at the same latitude with similar climates. Measurements of solar energy are usually expressed as total radiation on a horizontal surface, or on a surface that tracks the sun.

Radiation data from solar power (photovoltaic) systems are usually expressed in kilowatt-hours per square meter (kWh/㎡). Direct estimates of solar energy can also be expressed in watts per square meter (W/m2). Radiation data for solar hot water and space heating systems are typically expressed in British thermal units per square foot (Btu/ft²).
Want to know more about solar panels, welcome to pay attention to us our website, Guangdong Aurora Solar :www.teejoinsolar.com



