How Do Solar Panels Work?
Working Principle, Components & Efficiency Explained

How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through a physical and chemical process known as the photovoltaic (PV) effect. This technology allows solar energy to be transformed directly into usable electrical power for homes, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities.
Understanding how solar panels work helps system owners make informed decisions about panel selection, system design, and long-term energy performance.
The Photovoltaic Effect Explained
The photovoltaic effect is the fundamental principle behind solar power generation.
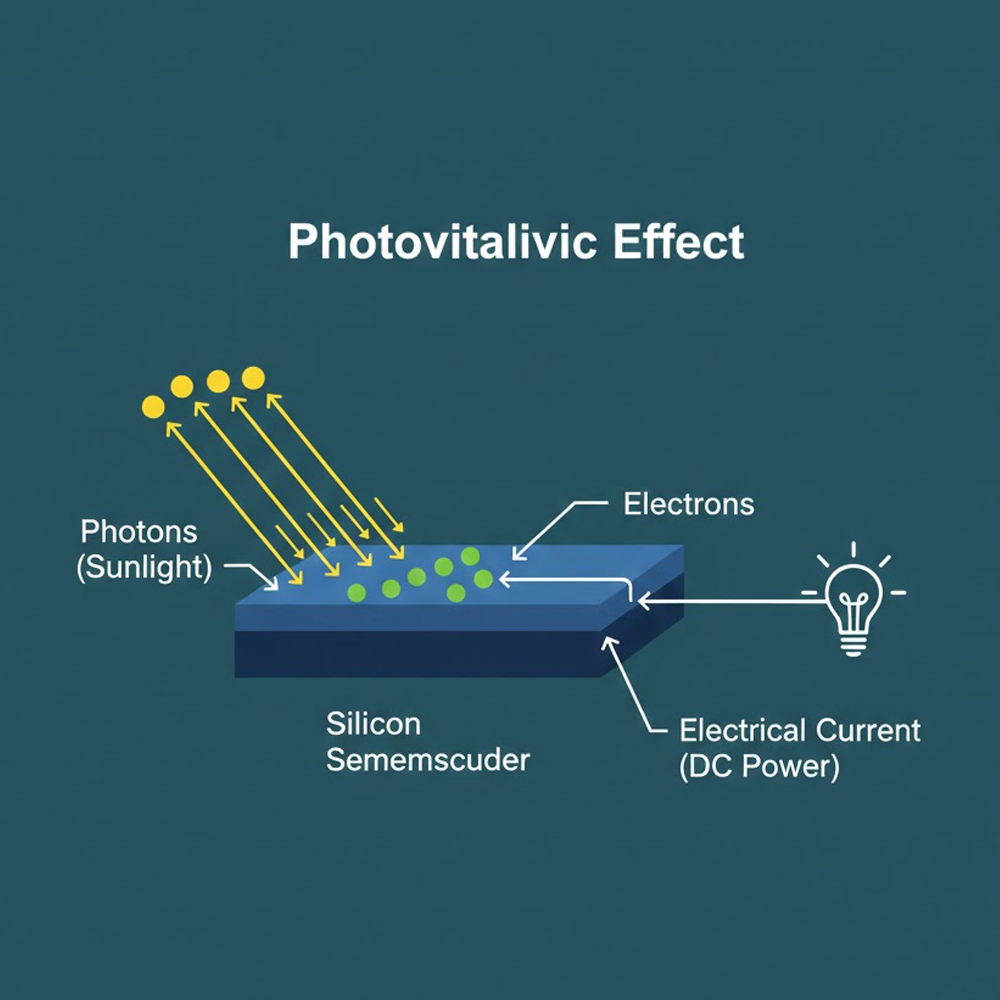
Solar panels are made up of multiple solar cells, typically manufactured from silicon, a semiconductor material. When sunlight strikes the surface of a solar cell, photons from the sunlight transfer energy to electrons inside the silicon structure.
This energy causes electrons to move, creating an electrical current. The current generated is direct current (DC) electricity, which flows through the internal circuitry of the solar panel.
This process occurs instantly whenever sunlight is available and requires no moving parts, making solar panels highly reliable and durable.
Main Components of a Solar Panel
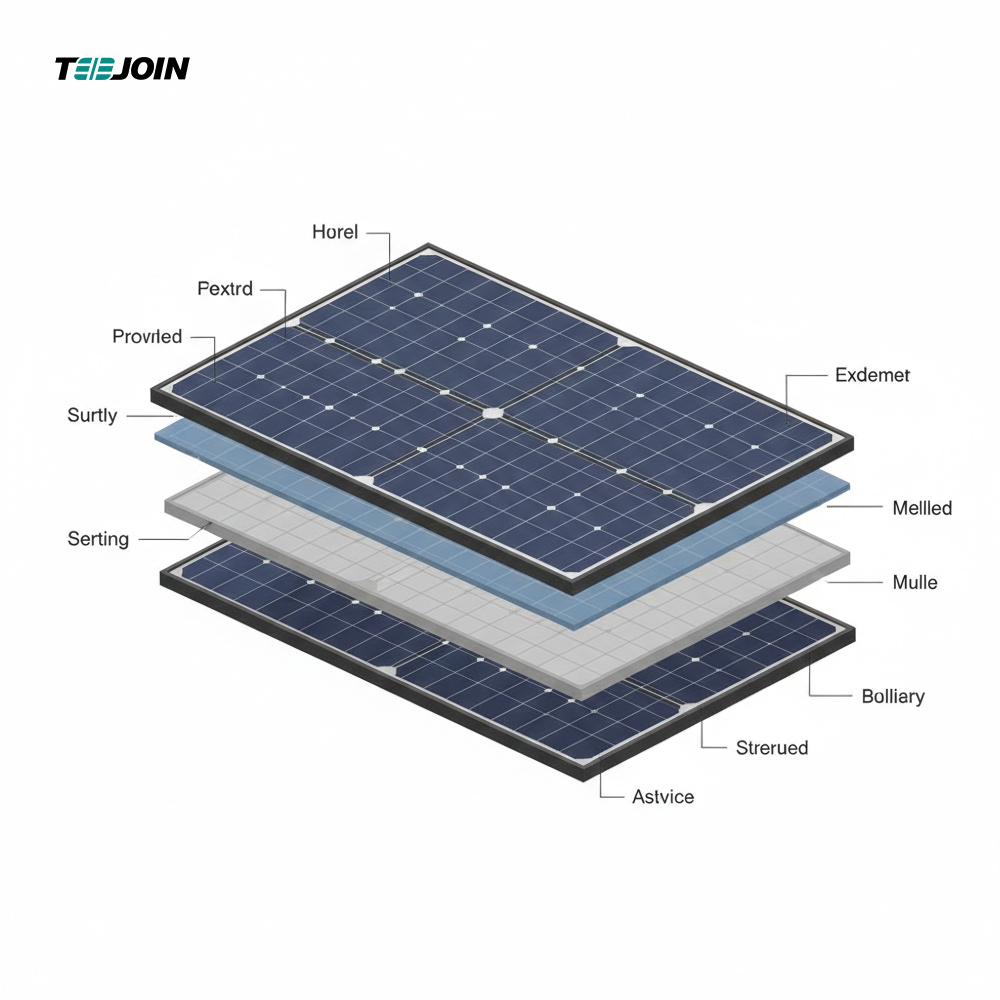

Each solar panel is composed of several layers, each playing a critical role in energy generation:
1. Glass Layer
The top tempered glass layer protects the solar cells from weather, impact, and environmental damage while allowing sunlight to pass through efficiently.
2. Anti-Reflective Coating
This coating reduces light reflection and increases sunlight absorption, improving overall panel efficiency.
3. Solar Cells
Solar cells are the core power-generating units. They are usually monocrystalline, polycrystalline, or bifacial cells, depending on design and application.
4. Encapsulation Layers
Encapsulation materials protect the cells from moisture, dust, and vibration, ensuring long-term reliability.
5. Back Sheet & Frame
The back sheet provides electrical insulation, while the aluminum frame adds mechanical strength and allows secure mounting.
From Solar Panels to Usable Electricity
The electricity produced by solar panels cannot be used directly by most appliances.
Once DC electricity is generated, it flows from the solar panels to a solar inverter, which converts DC power into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is the standard form used in homes, offices, and factories.
After conversion, the electricity is either:
Used immediately by connected loads
Stored in batteries (for hybrid or off-grid systems)
Exported to the utility grid (for on-grid systems)
This flexible energy flow allows solar systems to maximize energy utilization and cost savings.
What Affects Solar Panel Efficiency?
Solar panel efficiency refers to how effectively a panel converts sunlight into electricity. Several factors influence performance:
Cell Technology: Monocrystalline panels generally offer higher efficiency than polycrystalline panels.
Sunlight Intensity: More direct sunlight results in higher energy output.
Panel Orientation & Tilt: Proper installation angle maximizes exposure.
Temperature: Extremely high temperatures can slightly reduce efficiency.
Shading & Dust: Even partial shading can impact output significantly.
High-quality solar panels are designed to minimize performance loss under real-world conditions.
Types of Solar Panels

There are several common solar panel types used in modern solar power systems:
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Known for high efficiency, long lifespan, and sleek appearance. Ideal for residential and commercial rooftops.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Cost-effective solution suitable for large-scale installations with sufficient space.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Generate electricity from both front and rear sides, increasing overall energy yield in reflective environments.
Teejoin Solar manufactures multiple panel types to meet different project requirements and budgets.
How Solar Panels Perform Over Time
Solar panels are designed for long-term operation. Over time, they experience gradual performance degradation, typically around 0.5% per year.
This means that after 25 years, a high-quality solar panel can still operate at approximately 85–90% of its original output capacity.
Reliable manufacturers provide long-term performance warranties to ensure predictable energy production.
Applications of Solar Panels
Solar panels are widely used across different sectors:
Residential rooftop solar systems
Commercial buildings and offices
Industrial factories and warehouses
Solar farms and utility-scale projects
Off-grid and remote power systems
Their scalability makes solar panels suitable for both small and large energy demands.
Why Choose High-Quality Solar Panels?
Choosing high-quality solar panels ensures:
Higher energy yield over system lifetime
Better resistance to harsh weather conditions
Lower maintenance requirements
Stable long-term return on investment

Teejoin Solar applies strict quality control standards, international certifications, and advanced manufacturing processes to deliver reliable solar panels for global markets.
Conclusion
Solar panels work by harnessing sunlight and converting it into clean, usable electricity through the photovoltaic effect. By understanding how solar panels function, users can better design, select, and maintain solar power systems that deliver long-term performance and value.
With proper installation and quality components, solar panels remain one of the most efficient and sustainable energy solutions available today.



